Skin diseases are common health issues in India, affecting people of all ages. They can cause discomfort, itching, and sometimes serious health problems. Understanding these conditions helps in early detection and treatment, leading to healthier skin. This article discusses some common skin diseases in India, their causes, symptoms, and prevention methods.
Quick Overview of Common Skin Diseases in India
| Skin Disease | Description | Affected Areas |
|---|---|---|
| Acne | Pimples and blackheads due to clogged pores. | Face, shoulders, back |
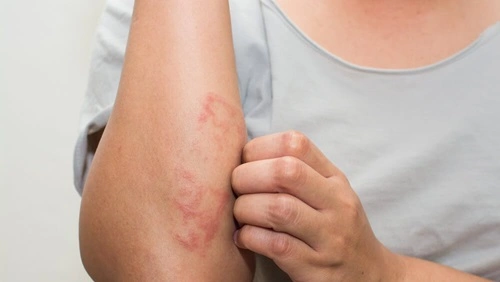
| Eczema | Red, itchy, inflamed skin patches. | Hands, face, neck |
| Psoriasis | Thick, red skin with silvery scales. | Elbows, knees, scalp |
| Fungal Infections | Ring-shaped rashes caused by fungi. | Feet, groin, body |
| Leprosy | Numb, pale skin patches; can cause nerve damage. | Skin, nerves |
| Scabies | Intense itching due to tiny mites burrowing into the skin. | Between fingers, wrists |
| Vitiligo | Loss of skin color in patches. | Face, hands, arms |
| Urticaria (Hives) | Raised, itchy welts on the skin. | Any part of the body |
| Dermatitis | Inflammation of the skin causing redness and itching. | Various body parts |
| Skin Allergies | Reactions causing redness, itching, and swelling due to allergens. | Face, hands, body |
Details About Each Skin Disease
1. Acne
Acne occurs when hair follicles become clogged with oil and dead skin cells, leading to pimples, blackheads, or whiteheads.
- Causes: Hormonal changes, oily skin, certain medications, and genetics.
- Symptoms: Pimples, blackheads, whiteheads, and sometimes cysts.
- Prevention: Keep the skin clean, avoid oily cosmetics, and eat a balanced diet.
2. Eczema
Eczema, or atopic dermatitis, is a condition that makes the skin red, inflamed, and itchy.
- Causes: Genetics, environmental factors, and allergens.
- Symptoms: Dry, itchy, and red patches on the skin.
- Prevention: Moisturize regularly, avoid known irritants, and wear soft fabrics.
3. Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic disease that causes red, scaly patches on the skin.
- Causes: Immune system issues, genetics, and triggers like stress or infections.
- Symptoms: Red patches with silvery scales, dry skin, and itching.
- Prevention: Manage stress, avoid skin injuries, and follow a healthy lifestyle.
4. Fungal Infections
Fungal infections, like ringworm, cause itchy, ring-shaped rashes.
- Causes: Fungi growing on the skin, often in warm, moist areas.
- Symptoms: Itchy, red, circular rashes with clear centers.
- Prevention: Keep the skin clean and dry, avoid sharing personal items, and wear breathable clothing.
5. Leprosy
Leprosy is a chronic infectious disease causing skin lesions and nerve damage.
- Causes: Bacteria called Mycobacterium leprae.
- Symptoms: Numb, pale skin patches, muscle weakness, and eye problems.
- Prevention: Early diagnosis and treatment; avoid close contact with untreated patients.
6. Scabies
Scabies is a skin infestation by tiny mites causing intense itching.
- Causes: Sarcoptes scabiei mites burrowing into the skin.
- Symptoms: Severe itching, especially at night, and thin burrow tracks on the skin.
- Prevention: Avoid direct skin contact with infected individuals and maintain good hygiene.
7. Vitiligo
Vitiligo causes loss of skin color in patches due to the destruction of pigment-producing cells.
- Causes: Autoimmune response, genetics, or triggers like sunburn.
- Symptoms: White patches on the skin, premature graying of hair.
- Prevention: Protect skin from sun exposure and avoid skin injuries.
8. Urticaria (Hives)
Urticaria involves raised, itchy welts on the skin, often due to an allergic reaction.
- Causes: Allergens, stress, infections, or certain medications.
- Symptoms: Red or skin-colored welts that vary in size and can merge together.
- Prevention: Identify and avoid triggers, wear loose clothing, and manage stress.
9. Dermatitis
- Symptoms: Red, swollen, and itchy skin that may blister or peel.
- Prevention: Avoid contact with known irritants or allergens, use mild soaps, and moisturize regularly.
- Note: Common forms include contact dermatitis (caused by allergens or irritants) and atopic dermatitis.
10. Skin Allergies
Skin allergies occur when the immune system reacts to allergens, causing irritation.
- Causes: Certain foods, insect bites, chemicals, plants, or medications.
- Symptoms: Redness, itching, swelling, and sometimes blisters.
- Prevention: Identify and avoid allergens, and use hypoallergenic products.
Government and Health Initiatives for Skin Diseases
The Indian government and healthcare organizations work to combat skin diseases through the following:
1. National Leprosy Eradication Programme (NLEP)
- Aims to eliminate leprosy as a public health problem in India.
- Provides free treatment and raises awareness about early diagnosis.
2. Health Awareness Campaigns
- Educate people about hygiene, skin health, and the prevention of infections.
- Promote awareness of fungal infections, scabies, and dermatitis.
3. Free Dermatology Camps
- Organized in rural and urban areas to provide free skin checkups and treatments.
- Help diagnose and treat conditions like vitiligo and psoriasis.
4. Affordable Medications and Treatments
- Subsidized or free medicines for conditions like fungal infections and leprosy are available in public healthcare centers.
Tips for Maintaining Healthy Skin
1. Maintain Hygiene
- Bathe regularly using mild soap and clean water.
- Avoid sharing personal items like towels or razors.
2. Eat a Balanced Diet
- Include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and proteins to nourish the skin from within.
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water.
3. Protect Skin from Sun Damage
- Use sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher to prevent sunburn and skin damage.
- Wear protective clothing and avoid direct sun exposure during peak hours.
4. Avoid Harsh Chemicals
- Use skin-friendly products and avoid harsh chemicals that can irritate the skin.
5. Seek Medical Help
- Consult a dermatologist if you notice persistent or unusual skin problems.
- Do not self-medicate as it may worsen the condition.
Conclusion
Skin diseases are common in India but can be managed or prevented with proper care and awareness. By maintaining hygiene, eating a healthy diet, and seeking timely medical help, we can reduce the burden of these conditions. Government initiatives and health programs play a vital role in educating and supporting people in managing skin health.
A little care goes a long way in keeping our skin healthy and glowing. Let’s work together to create awareness and ensure healthy skin for everyone!

